The future of manufacturing in 2023 and beyond: Four trends shaping the industry
The manufacturing industry is a constantly evolving industry experiencing a profound transformation, driven by rapid technological advancements and shifting consumer demands.
As we step into 2023 and beyond, it becomes increasingly evident that the future of manufacturing is not a distant vision but a tangible reality. Industry leaders and innovators are embracing cutting-edge trends that are shaping the landscape and revolutionizing traditional processes.
In today’s blog post, we dive into 4 major trends that are currently shaping its future and the impact that follows.
Let’s go!
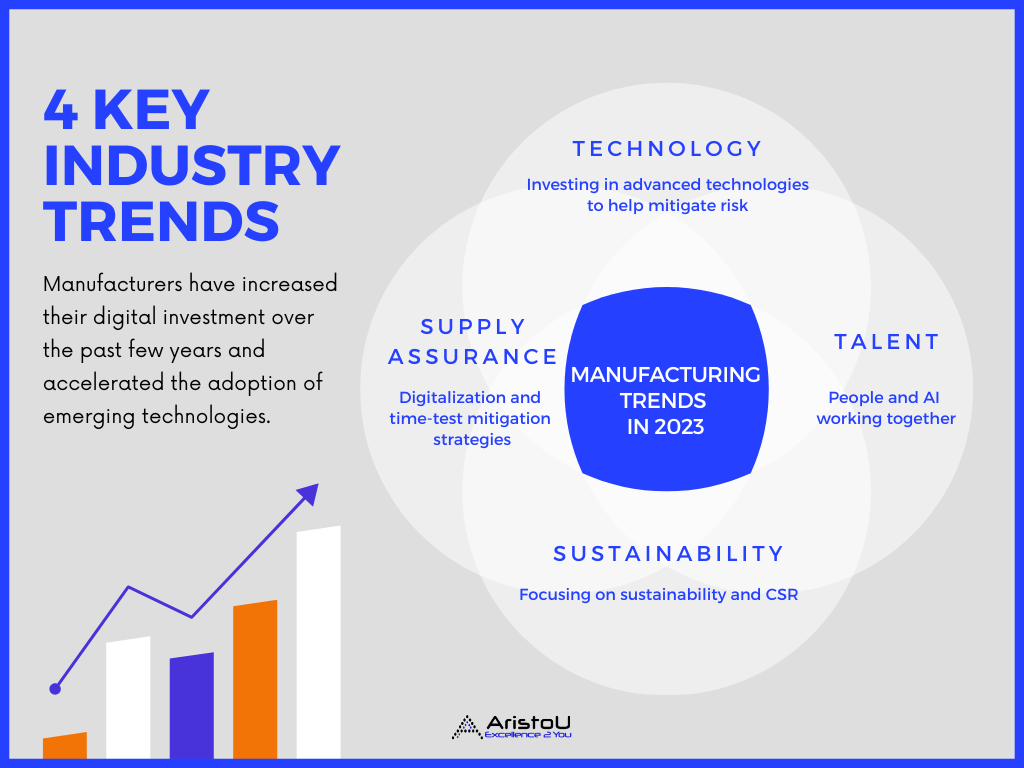
4 manufacturing industry trends to watch:
-
Technology: Investing in advanced technologies to help mitigate risk
-
Talent: People and AI working together harmoniously
-
Supply Assurance: Digitalization and time-tested mitigation strategies to achieve supply assurance
-
Sustainability: Focusing on sustainability and corporate social responsibility (CSR)
Let’s break down the above pointers in more depth below:
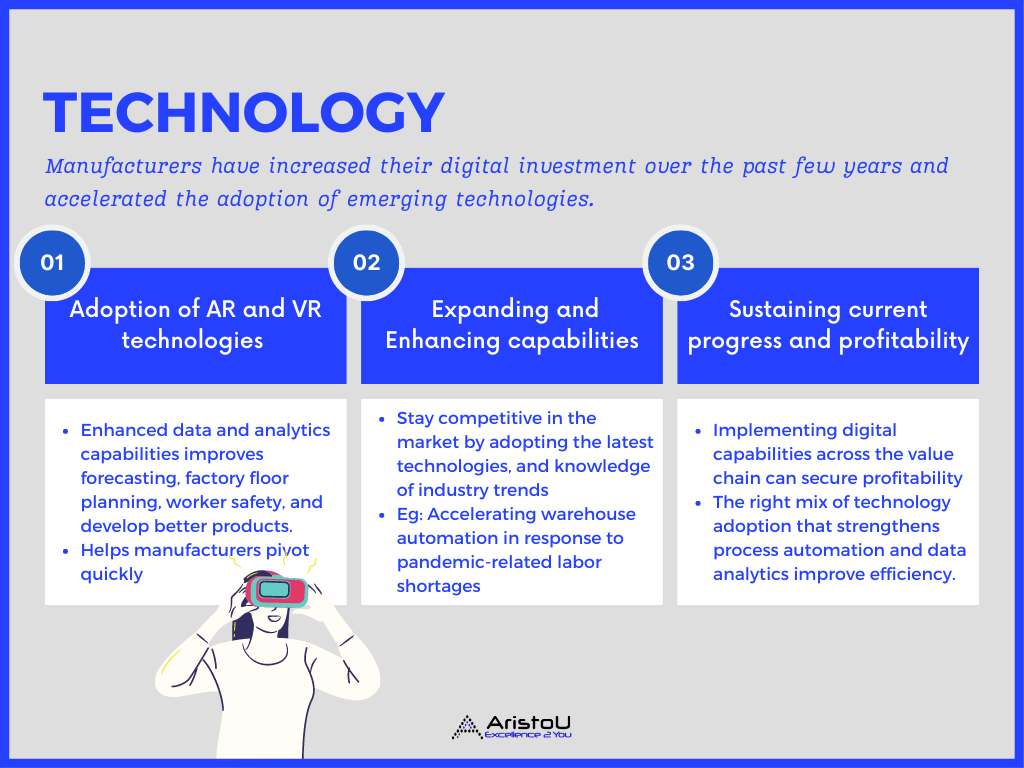
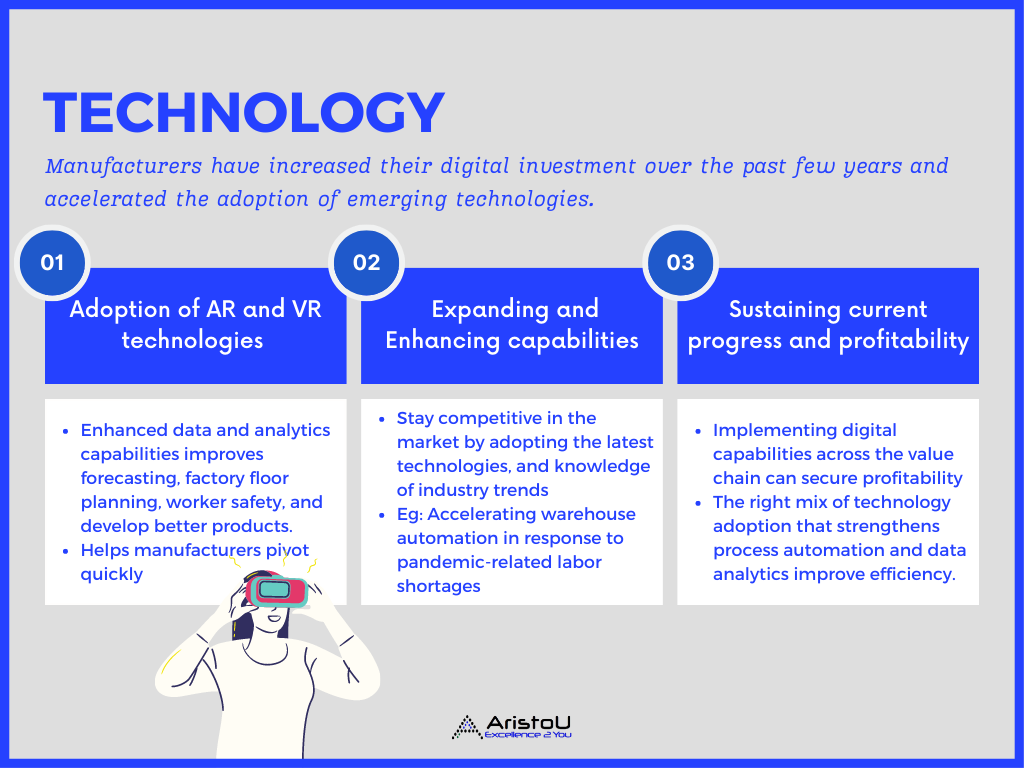
1. Technology: Investing in advanced technologies to help mitigate risk
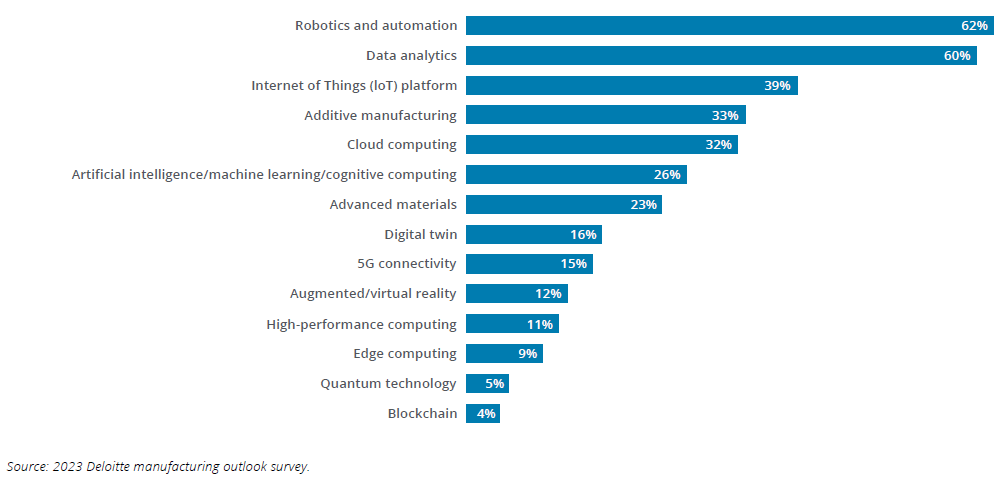
Manufacturers have increased their digital investment over the past few years and accelerated the adoption of emerging technologies (Deloitte 2023).
Companies with higher digital maturity have demonstrated greater resilience, similar to those that accelerated digitalization during the pandemic (Deloitte 2021). In such cases, companies were able to pivot faster than their peers with limited digital capabilities.
Likewise, companies with higher digital implementation tend to have increased supply chain visibility and are better equipped to manage supply chain challenges. The continuous investments in advanced manufacturing technologies can help manufacturers develop the required agility.
1A. Adoption of AR and VR technologies in manufacturing operations
-
-
Virtual technology (VR) has been viewed as an important strategy to stay competitive in the manufacturing marketplace.
-
Investments in AR and VR helps enhance operational efficiency, reduce errors, and improve productivity, and also aids manufacturers to pivot quickly.
-
Eg: Enhanced data and analytics capabilities can improve forecasting, improve factory floor planning, improved worker safety, better developed products.
-
-
-
Why is this important?
-
-
This is valuable in situations where travel is restricted or when experts are not physically present on-site.
-
By leveraging these technologies, manufacturers can tap into a global pool of expertise and ensure that their operations continue smoothly, even in challenging circumstances.
-
1B. Expanding and Enhancing capabilities in advanced manufacturing
-
-
Robotics and automation can enhance efficiency, whereas AI and ML capabilities can provide the required edge.
-
Increased automation is likely to drive productivity but also lead to changes in the design, prototyping and assembly processes.
-
Eg: some manufacturers have accelerated warehouse automation in response to pandemic-related labor shortages.
-
-
-
Why is it important?
-
-
Advanced manufacturing can improve efficiency, enhance product quality, reduce cost, provide opportunities for innovation and customization.
-
Also helps businesses stay competitive in the market by adopting the latest technologies, staying ahead of industry trends, and meeting customer expectations for quality and efficiency.
-
1C. Sustaining current progress and profitability in long run
-
-
Advanced technologies boost training, maintenance, and remote collaboration applications in manufacturing.
-
Implementing digital capabilities across the manufacturing value chain helps attain profitability and manufacturers have multiple levers to engage when it comes to digital sophistication.
-
The right mix of technology adoption that strengthens the core (process automation, data analytics) while also pushing the edges can improve efficiency.
-
-
Why is it important?
-
-
It is important because it ensures financial stability, competitive advantage, resilience in the face of challenges, talent attraction, customer trust, and enables long-term investment and growth.
-
It sets the foundation for continued success and helps manufacturing companies thrive in a dynamic and competitive industry.
-
2. Talent: People and AI working together harmoniously
2A. Upskilling and reskilling in AL and ML algorithms in manufacturing processes
-
As the use of digital technologies multiplies across the manufacturing sector, the workforce urgently requires advanced technical and digital skills. However, skilled workers are in short supply in the manufacturing industry (Mckinsey 2020).
-
Manufacturers emphasize on reskilling strategies, including continuous training to upskill the workforce, investment in startups to access new technology and talent, and collaboration with academic ecosystems to access digital skills.
-
Why is this important?
-
Upskilling in AL and ML algorithms in manufacturing processes enable companies to harness the full potential of AI and ML technologies.
-
It drives operational excellence, enables data-driven decision-making, fosters innovation, and ensures a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving industry.
-
2B. Advancements in predictive analytics and quality control
-
-
Advancements in predictive analytics and quality control have elevated the role of talent in the manufacturing industry.
-
This results in enhanced quality, cost reduction, competitive advantage, improves decision making, and creates talent empowerment.
-
This symbiotic relationship of domain knowledge and expertise between skilled professionals and AI technologies drives innovation, efficiency, and quality in manufacturing operations.
-
-
Why is this important?
-
-
The importance of advancements in predictive analytics and quality control lies in the ability to enhance product quality, reduce costs, gain competitive advantage, improve decision-making, empower talent, and drive continuous improvement in the manufacturing industry.
-
These factors collectively contribute to the success, growth, and sustainability of manufacturing companies in a highly competitive marketplace.
-
2C. Improve productivity, efficiency, and decision-making in manufacturing
-
-
The integration of human talent and AI technologies in manufacturing leads to improved productivity, efficiency, and decision-making.
-
The combination of human intelligence and AI technologies enables adaptive decision-making.
-
AI technologies role: AI-generated insights to evaluate multiple scenarios, assess risks, and select the best course of action.
-
Human intelligence role: provides contextual knowledge, ethical considerations, and the ability to make judgment calls in situations where human judgment is critical.
-
-
This collaborative decision-making approach enables manufacturers to respond quickly and effectively to changing market conditions and unforeseen challenges.
-
-
Why is it important?
-
-
This collaboration harnesses the strengths of both parties, leveraging human expertise, creativity, and adaptability alongside AI’s capabilities for data analysis, automation, and predictive insights.
-
By working harmoniously, people and AI drive innovation, optimize operations, and unlock new levels of performance in the manufacturing industry.
-
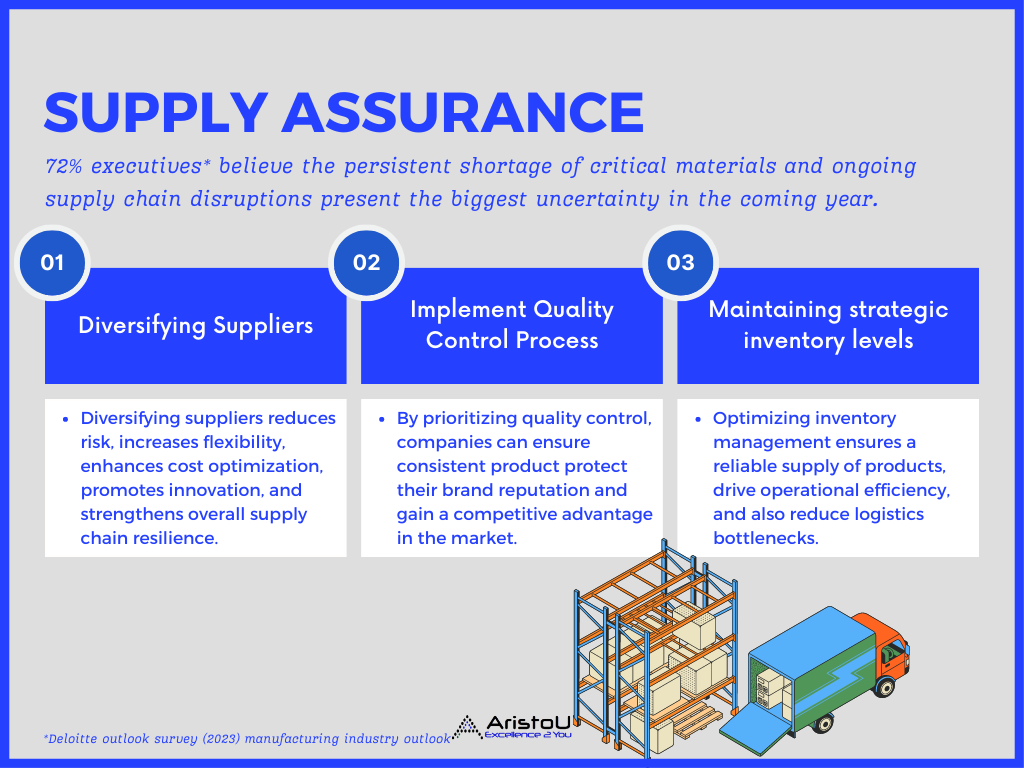
3. Supply Chain: Digitalization and time-tested mitigation stratgies to achieve supply assurance
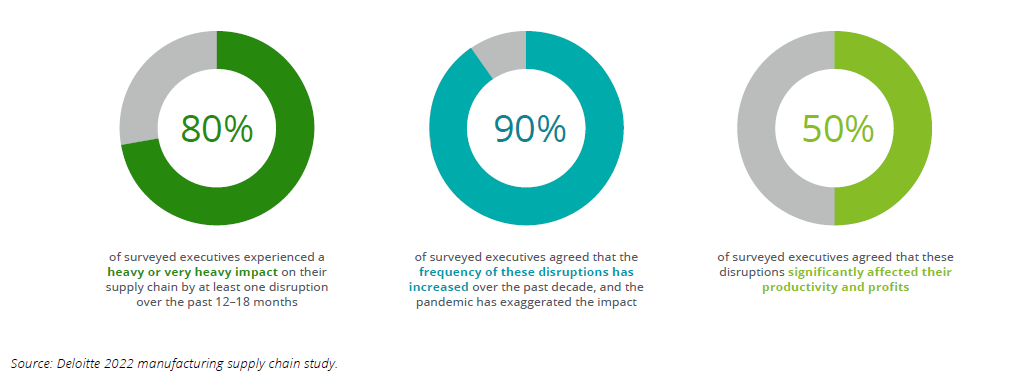
According to the Deloitte outlook survey (2022), 72% of surveyed executives believe the persistent shortage of critical materials and the ongoing supply chain disruptions present the biggest uncertainty for the industry in the coming year.
3A. Diversifying suppliers
-
-
Manufacturers are expected to continue diversifying their supplier base and adding redundancy in the coming year.
-
Supply chain executives should closely evaluate the cost of multiple suppliers versus the benefits of increased agility and risk mitigation.
-
For example, automotive company A chooses to engage with two different suppliers to meet its near-future production targets, whereas manufacturer B holds a long-term supply agreement with seven different suppliers across regions to ensure supply for its global production.
-
-
Why is this important?
-
-
Diversifying suppliers in the supply chain, supported by digitalization and time-tested mitigation strategies is essential for achieving supply assurance.
-
It reduces risk, increases flexibility, enhances cost optimization, promotes innovation, and strengthens overall supply chain resilience.
-
By embracing these practices, companies can better navigate uncertainties, maintain customer satisfaction, and drive long-term success in a dynamic business environment.
-
3B. Implementing quality control processes
-
-
One crucial aspect of supply chain digitization is the implementation of quality control processes. Quality control ensures that products meet predefined standards and customer expectations, reducing the risk of defects, recalls and customer dissatisfaction.
-
Businesses can employ advanced quality control technologies such as automated inspections, real time monitoring, and predictive analytics to identify and address quality issues promptly.
-
-
Why is this important?
-
-
This ensures consistent product quality, minimizes disruptions, reduces costs, enhances customer satisfaction, gains real-time visibility and drives continuous improvement.
-
By prioritizing quality control, companies can strengthen their supply chains, protect their brand reputation and gain a competitive advantage in the market.
-
3C. Maintaining strategic inventory levels
-
-
Many manufacturers have boosted local capacity by integrating their businesses across the value chain to reduce exposure to logistics issues and transportation bottlenecks.
-
-
Why is this important?
-
-
It helps manage demand fluctuations, mitigate supply chain disruptions, balance cost and service levels, improve supplier performance, and enhance overall supply chain agility and responsiveness.
-
By optimizing inventory management, companies can ensure a reliable supply of products, meet customer expectations, and drive operational efficiency in the supply chain.
-
4. Sustainability: Focusing on sustainability and corporate social responsibility (CSR)
4A. Increasing focus on sustainability and environmental responsibility
-
-
Manufacturing processes often have significant environmental footprints. Embracing sustainability involves reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste generation, implementing recycling initiatives, and adopting clean technologies.
-
Manufacturers can also explore renewable energy sources and optimize their supply chains to minimize carbon emissions.
-
-
Why is this important?
-
-
Besides protecting the earth, it helps meet stakeholder expectations, comply with regulations, achieve cost savings, foster innovation, enhance competitiveness, and ensure long-term business viability.
-
Integrating sustainability into their core business strategies allows manufacturers to create positive social and environmental outcomes while driving economic success.
-
4B. Implement Green Practices and renewable energy
-
-
Manufacturers can achieve significant environmental benefits, such as reduced greenhouse gas emissions, decreased energy consumption, minimized waste generation, and improved resource efficiency.
-
By diversifying energy sources, it reduces reliance on fossil fuels, and optimizes resource efficiency contributes to long-term sustainability and business continuity.
-
Embracing sustainable manufacturing practices also enhances brand reputation, attracts environmentally conscious customers.
-
-
Why is this important?
-
-
Building long term resilience: Climate change and resource scarcity pose significant risks to the manufacturing industry.
-
By adopting green practices and renewable energy, manufacturers can enhance their resilience and adaptability to future challenges and contribute to overall sustainability goals of society.
-
4C. Circular economy principles and closed-loop manufacturing approaches
-
Both circular economy principles and closed-loop manufacturing approaches aim to shift from the traditional linear “take-make-dispose” model to more sustainable, resource-efficient, and environmentally friendly systems.
-
The circular economy is based on three principles, driven by design:
-
Eliminate waste and pollution
-
Circulate products and materials (at their highest value)
-
Regenerate nature
-
-
Closed Loop manufacturing is materials used in production that can be reused. Closing the loop entails that any post-consumer waste is recollected and reused to start the process all over again.
-
-
Why is this important?
-
There is value here for both a business’s bottom line and global sustainability.
-
According to research (2017), the fashion industry will use up more than 26% of the world’s entire carbon budget by 2050 at our current pace.
-
These concepts promotes the reuse, recycling, and repurposing of materials to create a regenerative and restorative economy that reduces waste, conserves resources, and fosters long-term sustainability.

Looking to the Future: Embracing Growth Despite Projected Challenges in the Manufacturing Industry
So…what’s next?
The manufacturing industry is set for growth and transformation despite the anticipated challenges.
By embracing technological advancements, strengthening supply chains, adopting sustainable practices, and fostering global collaboration, manufacturers can position themselves for success in 2023 and beyond.
The future of manufacturing in 2023 is characterized by a convergence of disruptive technologies and a shift towards sustainable practices.
1. AI and machine learning are enhancing efficiency
-
AL and ML empower manufacturers to optimize operations, improve productivity, and make data-driven decisions that drive profitability.
2. 3D printing enables unprecedented customization.
-
3D printing is emerging as a game-changer, offering manufacturers opportunities for customization. Businesses can create complex and intricate designs, reduce lead times, and minimize waste.
-
The ability to rapidly prototype and produce customized parts opens up new avenues for product development and supply chain optimization.
3. IoT (Internet of Things) to improve maintenance
-
By connecting machines, sensors, and devices, manufacturers gain real-time visibility and control over their operations.
-
IoT enables proactive maintenance, remote monitoring, and predictive analytics. This enhances overall efficiency, reduces downtime, and optimizes resource allocation.









Leave a Reply